Climate Change: Global Warming Causing Arctic Melt Season to Increase By Five Days Every Decade

Global warming is causing the melt season across the Arctic to increase by five days every decade, scientists have warned.
Research by University College London (UCL) Earth Sciences has confirmed Arctic ice trends showing how the sea ice appears later in the autumn every year.
In some parts of the Arctic, the autumn freeze takes place 11 days later than it did 10 years ago.
Published in the upcoming issue of the journal Geophysical Research Letters, the researchers say their study has big implications for looking at the effects of climate change, as well as providing useful information for shipping paths that will be created in the future.
Researcher Julienne Stroeve said: "The extent of sea ice in the Arctic has been declining for the last four decades and the timing of when melt begins and ends has a large impact on the amount of ice lost each summer.
"With the Arctic region becoming more accessible for long periods of time, there is a growing need for improved prediction of when the ice retreats and reforms in winter."
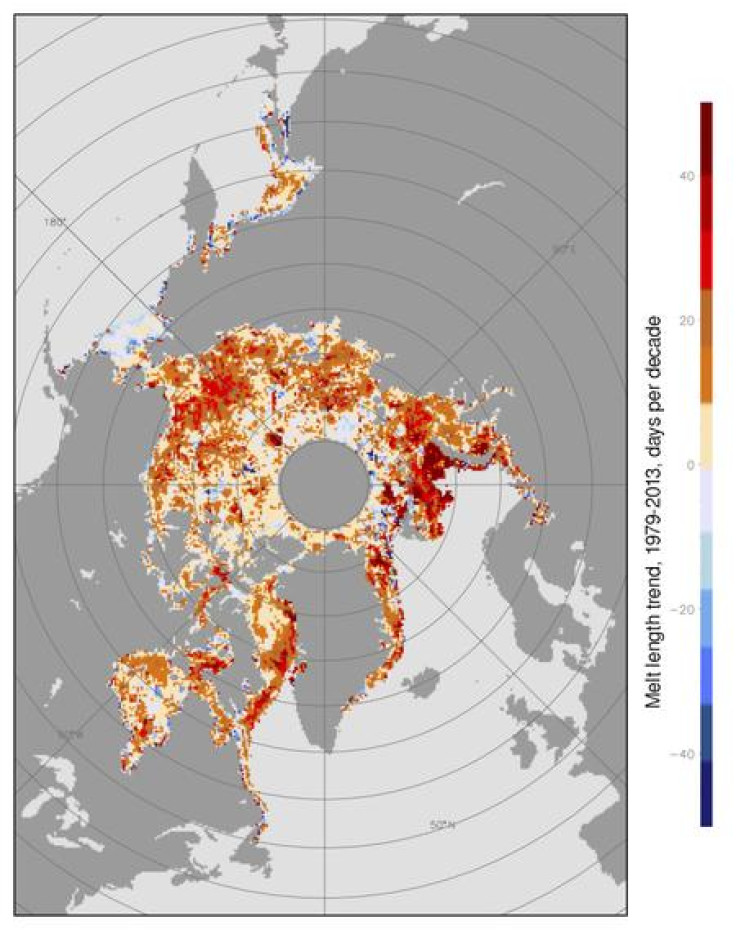
The timing of the Arctic melt influences how much of the sun's energy will be absorbed by the ice and sea, which in turn affects how reflective the surface is.
Icy surfaces have a high albedo and reflect incoming heat back into space, while water has a low albedo, meaning it absorbs heat from the sun.
A drop in the amount of sea ice causes changes in atmospheric temperature. By analysing the albedo from the last 30 years, the researchers were able to update trends and add six years' worth of data onto existing analysis.
Their new findings confirm existing data trends showing longer melt seasons across the Arctic.
"The headline figure of five days per decade hides a lot of variability. From year to year, the onset and freeze-up of sea ice can vary by about a week," Stroeve said.
"There are also strong variations in the total length of the melt season from region to region: up to 13 days per decade in the Chukchi Sea, while in one, the Sea of Okhotsk, the melt season is actually getting shorter."
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.






