Anger, reflection as N.Ireland marks 50 years since 'Bloody Sunday'
British Prime Minister Boris Johnson this week called "Bloody Sunday" a "tragic day in our history".
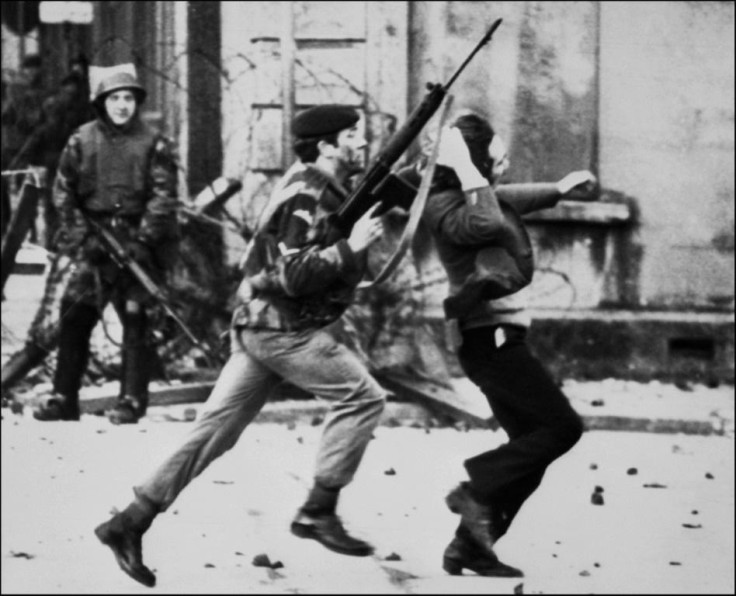
Relatives of 13 civil rights protesters shot dead in Northern Ireland by British soldiers 50 years ago demanded justice on Sunday, as they commemorated one of the darkest days in modern UK history.
The "Bloody Sunday" victims' names were read out under a leaden sky to the mournful notes of an Irish flute, as the relatives and hundreds of supporters gathered for a memorial service in the city of Londonderry -- known as Derry to pro-Irish nationalists.
Earlier, many had retraced a peaceful march through the divided city that ended in carnage on January 30, 1972, when the protesters had set out to demand Catholic rights against the city's Protestant minority.

From U2, Bono and The Edge released on social media an acoustic version of "Sunday Bloody Sunday", the Irish band's iconic song about the day.
A performance of music and poetry hosted by actor Adrian Dunbar, from TV police drama "Line of Duty", included a choral rendition of the US civil rights anthem "We Shall Overcome" -- which was also sung by the 1972 marchers.
Michael McKinney, whose brother William was among those killed, said the UK government was "scared" of allowing any prosecutions of the soldiers for fear of what a trial might uncover.
But addressing the remembrance service, he stressed: "We will not go away and we will not be silenced. We shall overcome."

At the head of Sunday's procession were 14 children each bearing a white rose -- a 14th man who was shot died months later, although an official inquiry said his death was unrelated to his wounds.
The children were followed by older relatives carrying portraits of those killed by members of the British Army's feared Parachute Regiment.
Some of the victims were shot in the back, or while on the ground, or while waving white handkerchiefs, as more than 100 high-velocity rounds ripped across the city's Catholic Bogside district.
The yearly memorial service was attended for the first time by an Irish premier, as Taoiseach Micheal Martin joined other dignitaries in laying a wreath at an obelisk commemorating the 14.
"I believe that the full process and justice of the courts should be deployed," Martin told reporters after meeting the relatives in private.
"It is important because time is moving on too for many, many families, and families need closure."
British Prime Minister Boris Johnson this week called "Bloody Sunday" a "tragic day in our history".
But his government is pushing legislation that critics say amounts to an amnesty for all killings during Northern Ireland's three decades of sectarian unrest, including by security forces.
After an initial government report largely exonerated the paratroopers and authorities, a 12-year inquiry found in 2010 that the victims were unarmed and posed no threat, and that the soldiers' commander on the ground violated his orders.
The mammoth inquiry, whose report ran to 5,000 pages, prompted then prime minister David Cameron to issue a landmark apology in parliament.
He agreed with its finding that the killings were "unjustified and unjustifiable".
One paratrooper, "Soldier F," was charged with murder in 2019. But prosecutors dropped the case last year after determining that the evidence against him would not be permissible in a court.
Michael McKinney is seeking a judicial review of the prosecutors' decision.
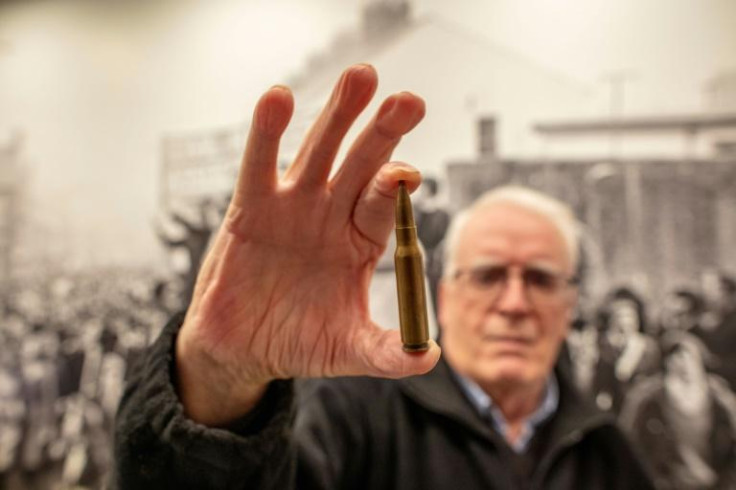
Charlie Nash, now 73, saw his 19-year-old cousin William Nash killed on "Bloody Sunday".
"It's important for the rest of the world to see what they done to us that day. But will we ever see justice?" he told AFP.
"Never, especially not from Boris Johnson," Nash added.
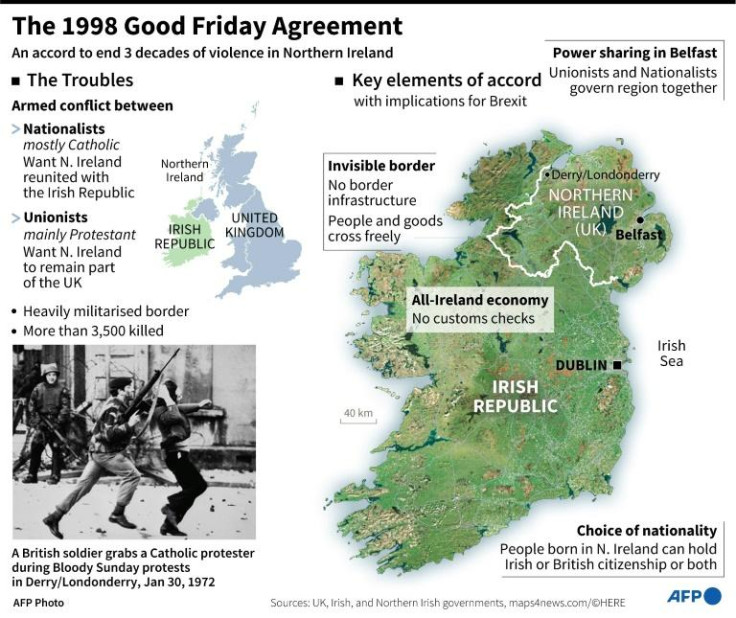
In Northern Ireland, new tensions today surround the UK's fractious divorce from the European Union.
Protestant unionists want Johnson's government to scrap a protocol governing post-Brexit trade for the province, which treats Northern Ireland differently from the UK mainland.
"Northern Ireland finds itself again in the eye of a political storm where we appear to be collateral damage for a prime minister whose future is hanging in the balance," said professor Deirdre Heenan, a Londonderry resident who teaches social policy at Ulster University.
Copyright AFP. All rights reserved.
This article is copyrighted by International Business Times, the business news leader





