China faces gigantic debt pile amounting to 282% of GDP

China's total debt has quadrupled since 2007 to reach $28tn (£18.1tn, €24.9tn) by mid-2014, amounting to 282% of the country's current gross domestic product, a report from the McKinsey Global Institute shows.
The report says the huge debt – larger than that of the US and Germany combined – is fuelled by real estate and shadow banking in the country.
It added that half of all loans are linked, directly or indirectly, to China's overheated real estate market. Further, unregulated shadow banking accounts for nearly half of new lending, and the debt of many local governments is probably unsustainable.
While the borrowing of the central government is low by global standards, local governments have borrowed heavily via vehicles after the global financial crisis and now working hard to repay the debt.
The real estate sector, which borrowed heavily during the boom period in China, is now looking at China's central bank, People's Bank of China, to relax monetary policy to boost demand.
However, McKinsey says China's government has the capacity to bail out the financial sector in case of a property related debt crisis. The challenge will be to contain future debt increases and reduce the risks of such a crisis, without putting the brakes on economic growth, according to the institute.
The challenge will be to contain future debt increases and reduce the risks of such a crisis, without putting the brakes on economic growth, according to the institute.
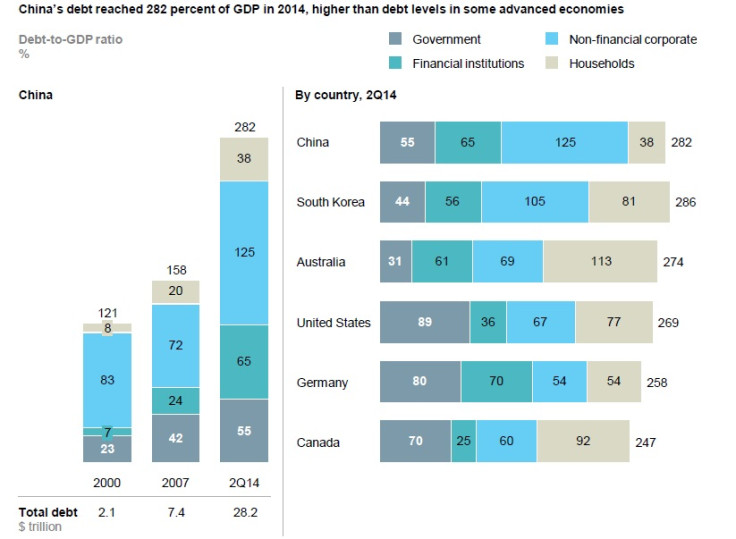
About 30% of the loan burden is expected to have come from the country's shadow-banking system, which has come under the government scanner due to transparency concerns.
In April, China's Baoding Tianwei Baobian Electric (BTBE) became the first state-owned firm to default on a bond, as the power company's deadline to make interest payment passed.
BTBE is a subsidiary of the Baoding Tianwei Group, which owns 23% of the listed entity. Baoding Tianwei Group is in turn entirely owned by the Beijing-based China South Industries Group Corp, which is a major defence equipment producer, owned by the central government.
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.






















