Harvard Study: E-Cigarettes Not 'Gateway' to Smoking

Electronic cigarettes are not a "gateway" to smoking normal cigarettes with just 1% of non-smokers having tried them, according to the largest ever EU study published on the subject.
The findings in the Journal of Tobacco Studies, which assessed 26,500 consumers across Europe, "verifies" that vapers will not move onto conventional cigarettes.
Researchers from the Harvard School of Public Health found e-cigarette users were mostly young aged between 15 and 24 and were heavy smokers who switched to electronic cigs in order to quit real ones.
Some 20% of smokers tried an e-cigarette at least once compared to 4% of former smokers while only 1.1% of non-smokers had used an e-cigarette.
The Harvard study estimates that 29 million Europeans have tried an e-cigarette.
Konstantinos Farsalinos, cardiologist at the Onassis Cardiac Surgery Centre in Athens, told the New Scientist: "This study verifies that e-cigarette use does not renormalise smoking. The results show minimal adoption by non-smokers."
It endorses a report by Public Health England in May that switching to electronic cigarettes as an alternative and "much safer" source of nicotine has enormous potential to reach smokers. It also stated e-cigarettes and other nicotine devices offered vast potential health benefits and that the opportunity "should not be missed" with proper regulation to be part of public health policy.
The controversy over the use of e-cigarettes has, however, divided opinion.
Kelly Evans from Social Change UK also conducted a study involving girls aged 11 to 12 years in North Wales and found advertising in e-cigarettes promoted them as cool products, not as a device to give up smoking. She found some offered flavours such as strawberry milkshake and gummy bear to attract youngsters.
"I've contacted some companies that provide these flavours and their response has been, 'Well, adults like gummy bears too'.
"My research with young people and children shows they are tempted by these flavours."
What is an E-Cigarette?
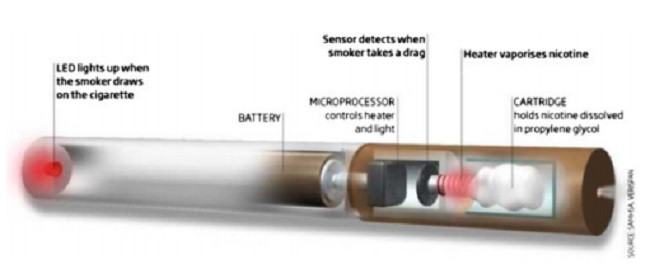
Electronic cigarettes (also known as e-cigarettes or electronic nicotine delivery systems)
were invented in China in 2003 and designed to provide inhaled doses of vaporised nicotine.
Electronic cigarettes were first introduced to Europe in 2005 and have become increasingly popular sinceElectronic cigarettes are composed of a re-chargeable lithium ion battery, and a battery powered atomiser which produces vapour by heating a solution of nicotine, usually in propylene glycol or glycerine, held in a (often refillable) cartridge in the device
Drawing air through the e-cigarette triggers the heater to create vapour which
contains nicotine and is inhaled by a smoker the same way as smoke from
conventional cigarettes.Producing nicotine vapour from a solution rather than by burning tobacco means that electronic cigarette vapour is free from almost all of the many toxic chemicals that accompany nicotine in cigarette smoke.
Not all electronic cigarettes include nicotine; some simply produce vapour for inhalation, but these are not popular among users.
Source: Public Health England
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.




















