World Refugee Day 2017: Crisis in South Sudan, world's fastest growing refugee emergency
Aid agencies are struggling to provide food and services in South Sudan due to a funding crisis.
The number of people who were forced from their homes due to conflict or persecution by the end of 2016 was a record 65.6 million people. That's more than the population of Britain. More than half of refugees globally come from just three countries: Syria, Afghanistan and South Sudan, which have been war-torn for years. Globally, Syrians still represent the largest forcibly displaced population with 12 million – or 65 percent of its population.
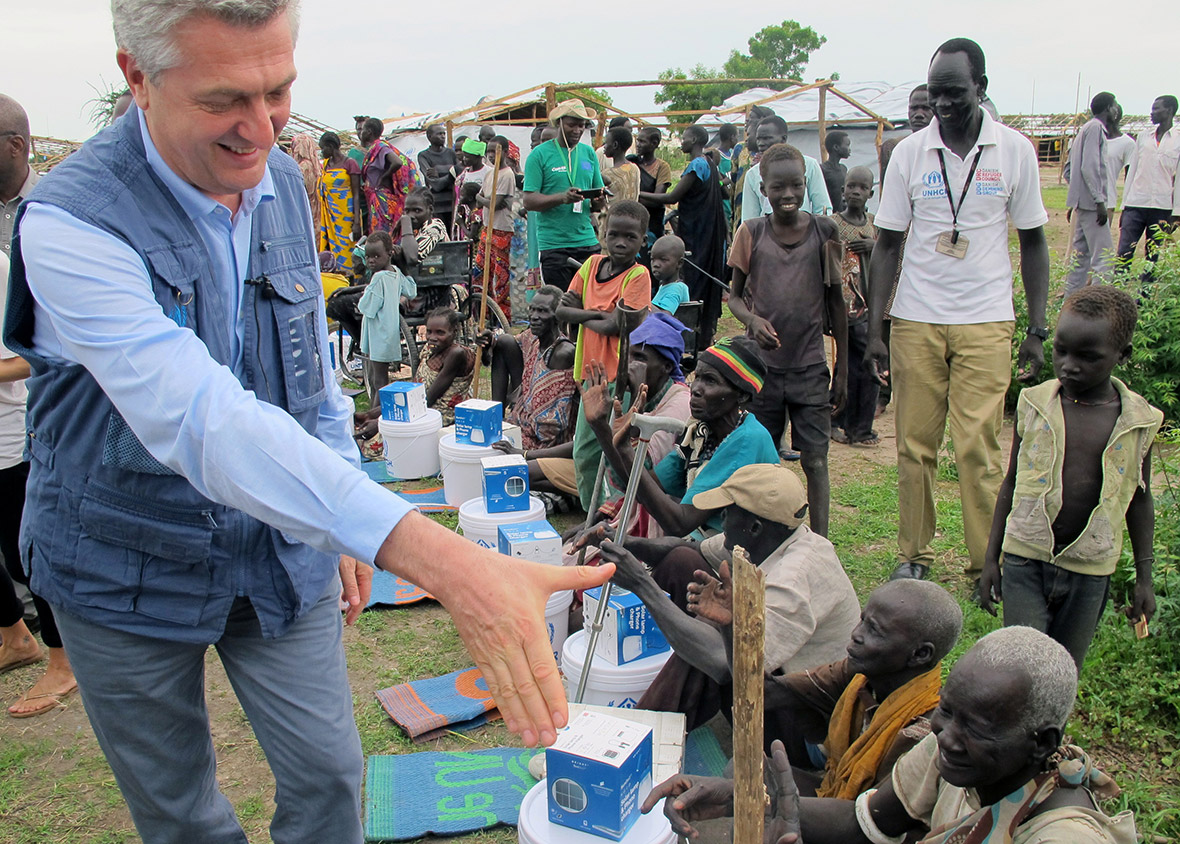
However, the world's fastest growing refugee crisis is in South Sudan. More than three million people, or a third of its population, have fled their homes, creating Africa's biggest refugee crisis since the Rwandan genocide. Filippo Grandi, the head of the UN's UNHCR refugee agency, said South Sudan's combination of violence, ethnic strife, lack of development, climatic factors and international neglect is unmatched anywhere in the world.

Grandi, who visited a camp for displaced people in South Sudan ahead of World Refugee Day (Tuesday 20 June 2017) called on the country's leadership to help stem the flow of people from within its borders. He said world powers must step up pressure on South Sudan's warring parties to go back to talks on ending a civil war that has forced about a third of the population to flee.
The fledgling nation's civil war erupted out of political infighting in late 2013, just two years after South Sudan declared independence from Sudan and took over running its own affairs. Experts say the conflict in some areas amounts to ethnic cleansing and risks escalating to genocide.
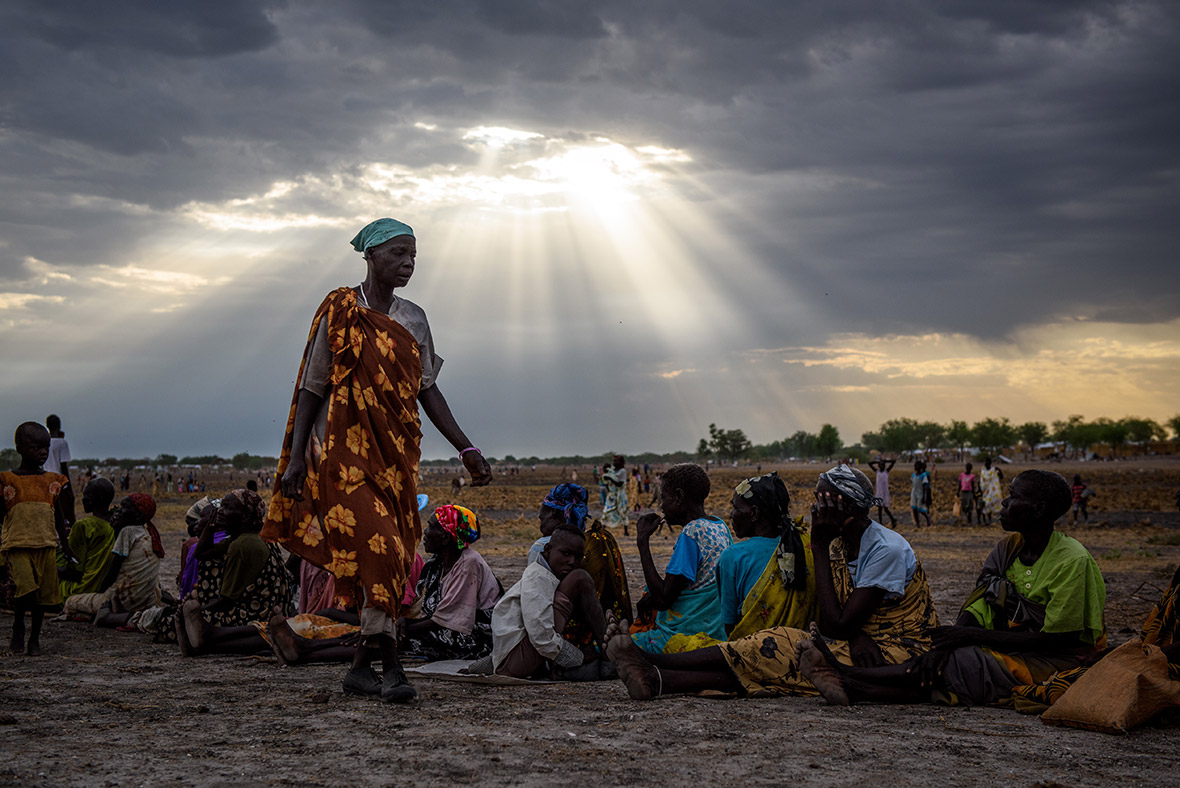
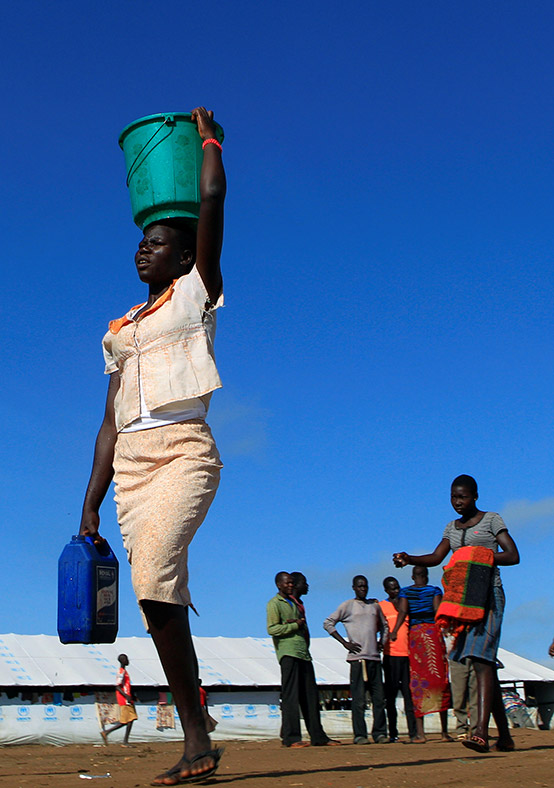
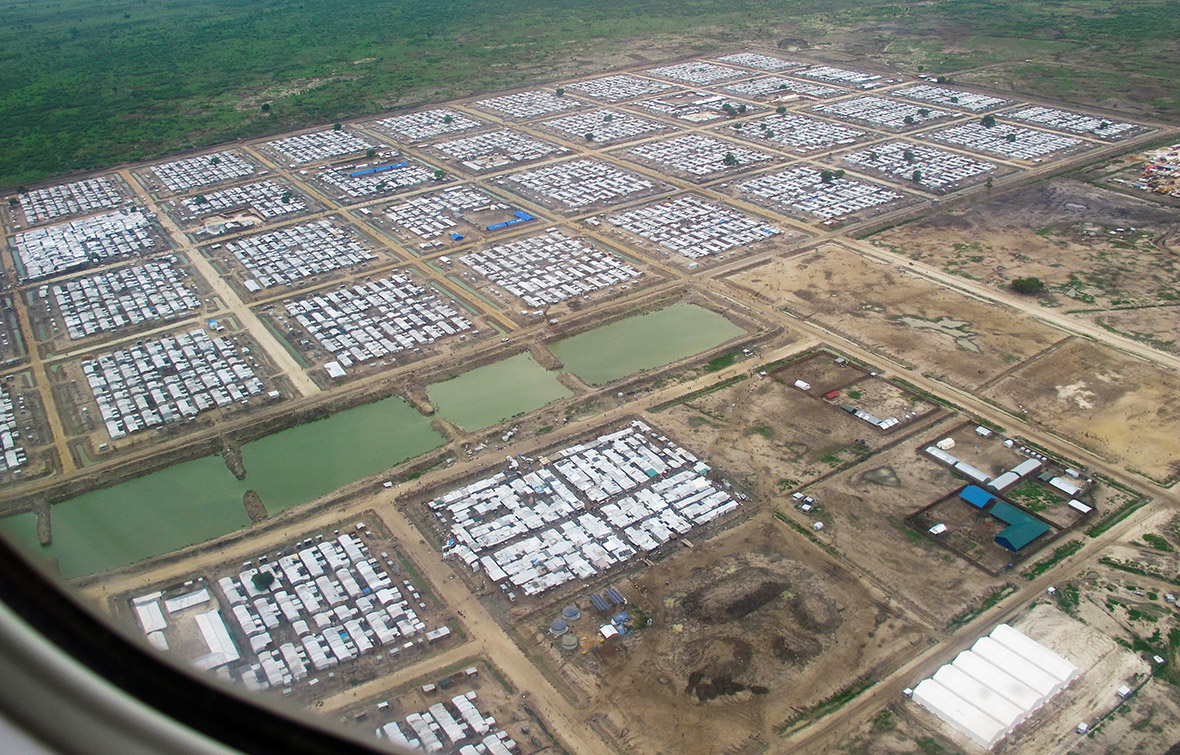




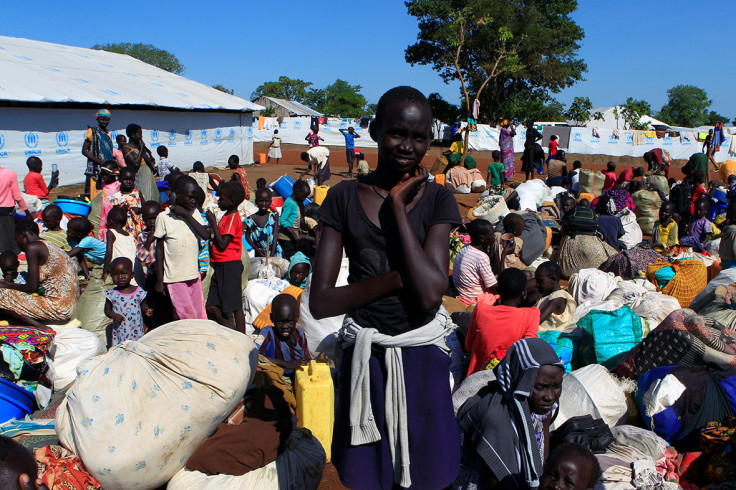
Children make up 62 per cent of the refugees from South Sudan, according to the latest UN figures. The trauma, physical upheaval, fear and stress experienced by so many children account for just part of toll the crisis is exacting. Children remain at risk of recruitment by armed forces and groups and, with traditional social structures damaged, they are also increasingly vulnerable to violence, sexual abuse and exploitation.
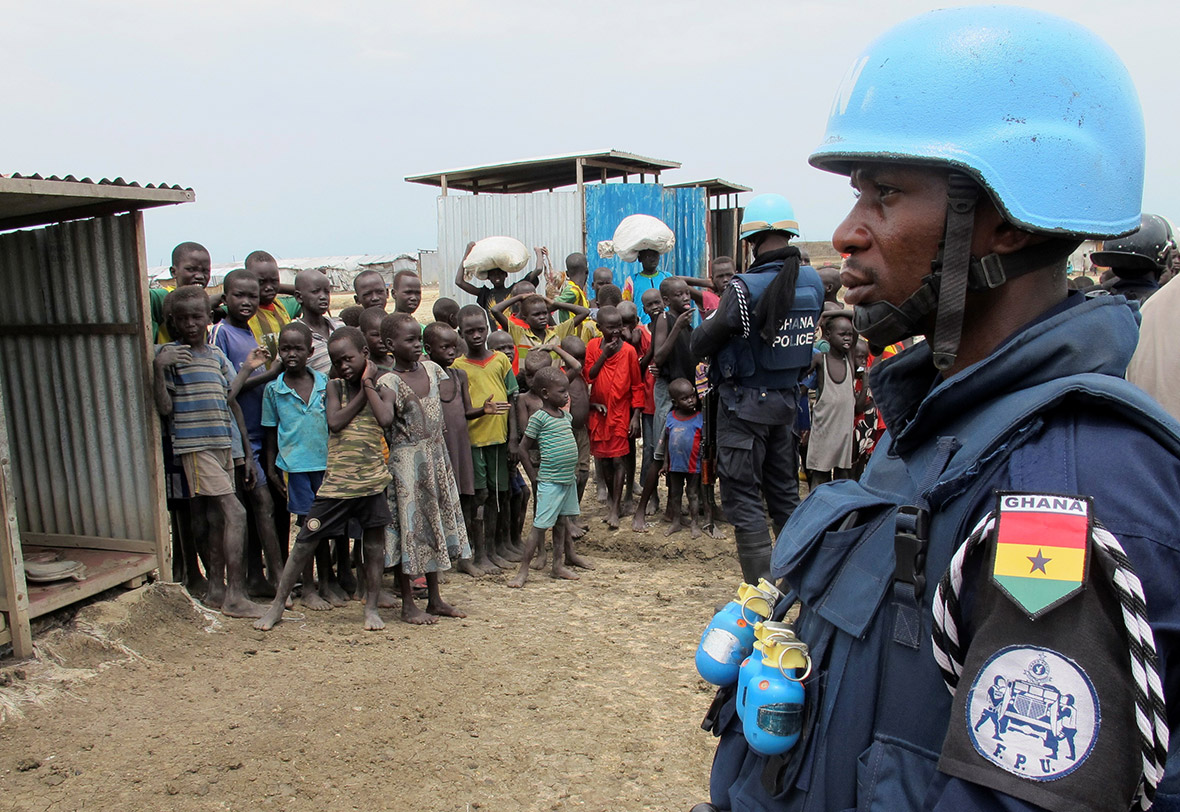
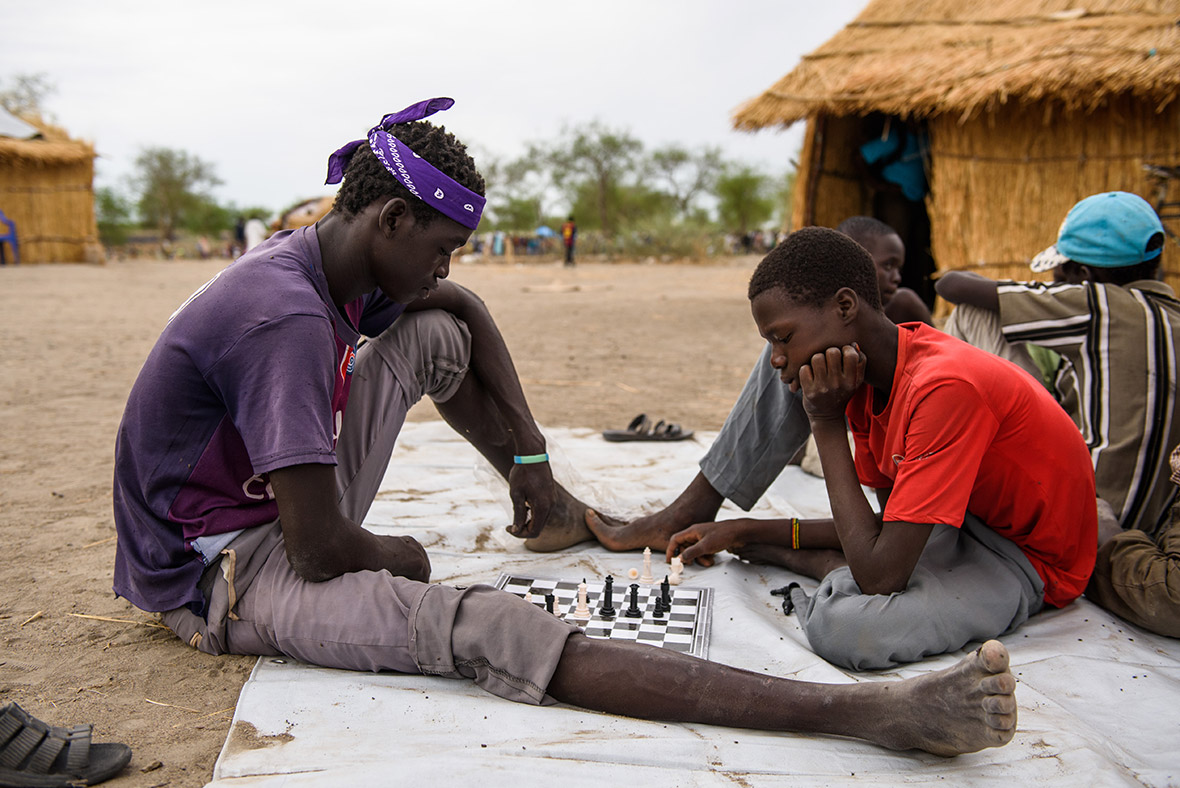
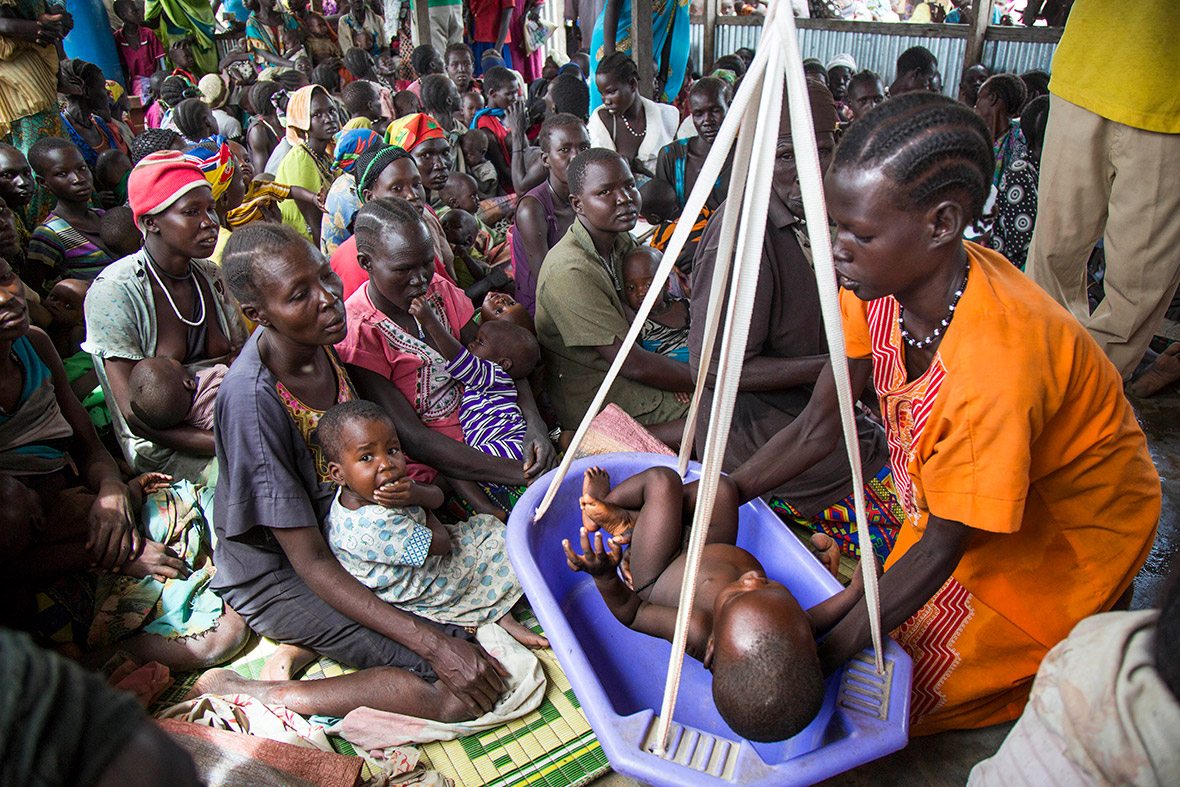



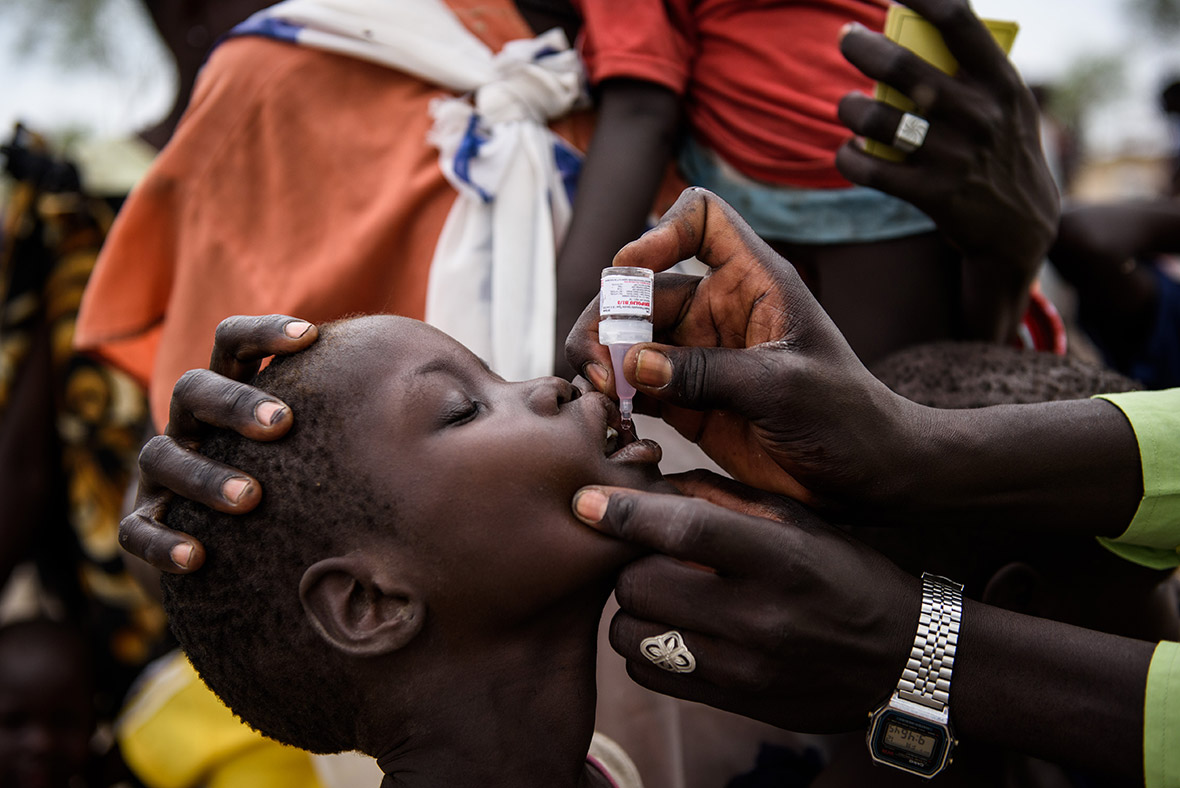
Refugee families fleeing to neighbouring countries in search of shelter and safety are facing a double catastrophe this rainy season, with children most at risk from the health and protection risks associated with inadequate shelter. Much greater support is needed to ensure that every refugee family has somewhere safe to live, as well as urgent humanitarian assistance including food, water, protection, education and medical care.
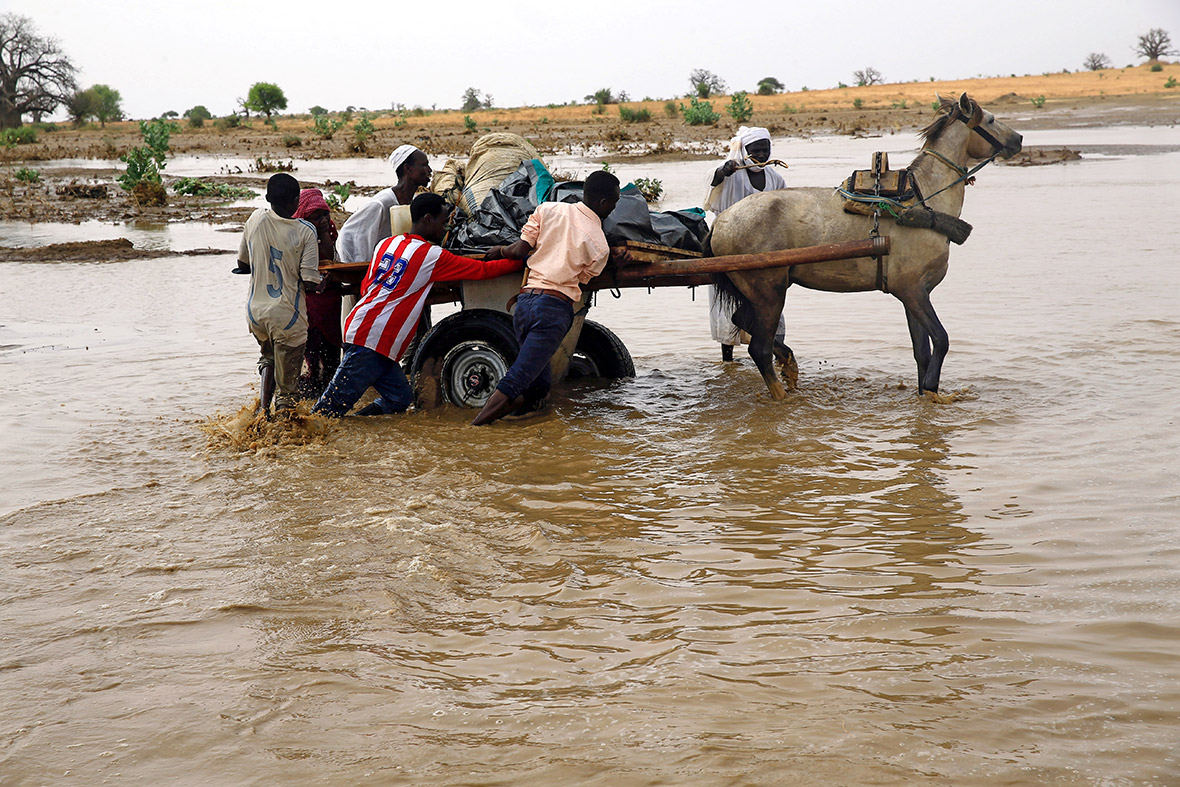
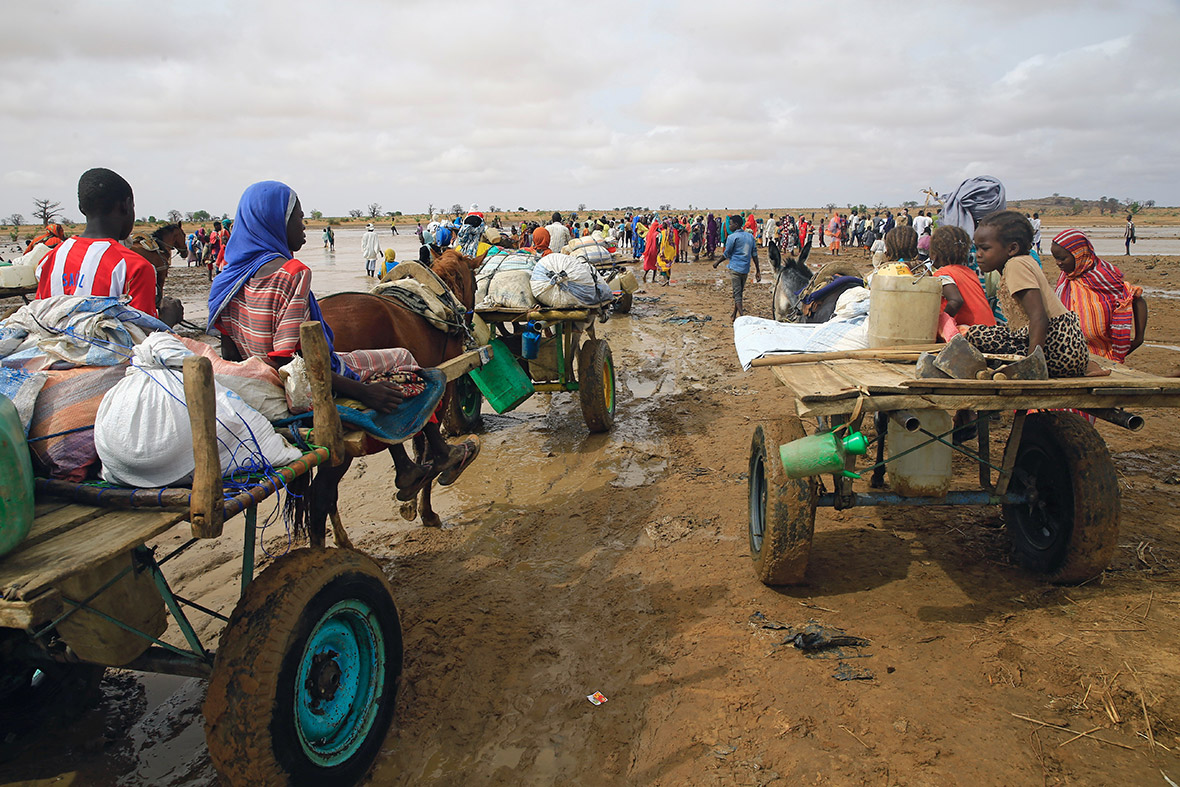
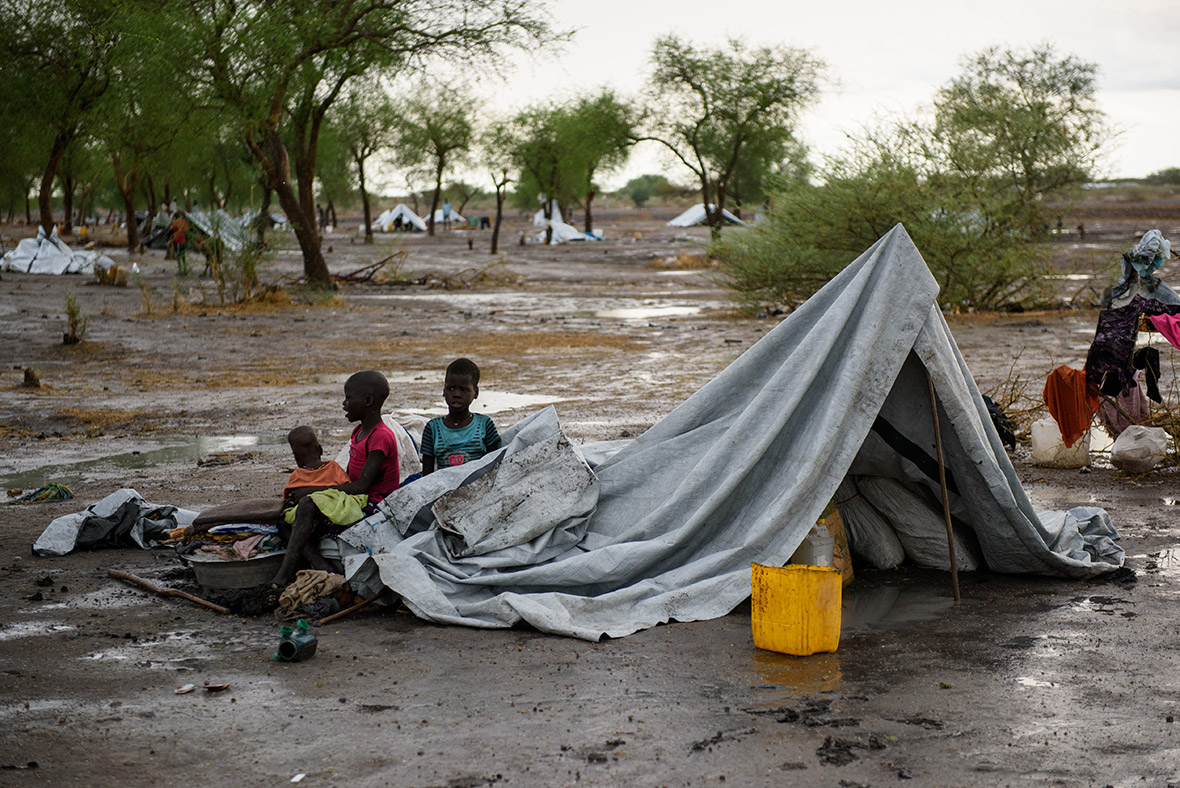



Aid workers are struggling to raise funds for South Sudan, partly because of frustrations over the lack of progress in peace talks and partly because the scale of the problem is hidden, Grandi said. "They (South Sudan's refugees) don't arrive on the shores of Europe, or Australia or at the border between Mexico and the US Those are the places where refugees become visible and their voices are heard," he said.
Humanitarian groups fear donor fatigue is weighing on efforts to meet requirements. Famine in northeast Nigeria, together with South Sudan, Yemen and Somalia, constitute the worst humanitarian crisis the world has faced since 1945, the UN said in March. "There is donor fatigue because there are a lot of crises," said Ahmed Al Meraikhi, the UN Secretary-General's humanitarian envoy.
The funding crisis has compelled the United Nations to halve the food rations given to South Sudanese refugees living in camps in Uganda. The World Food Programme (WFP) was forced to cut monthly rations from 12kg of maize a month to 6kg. The cuts came nearly two months after the UN warned the situation was at breaking point. "There is just not enough money to feed them," said Lydia Wamala, spokeswoman for the UN food agency in Uganda.
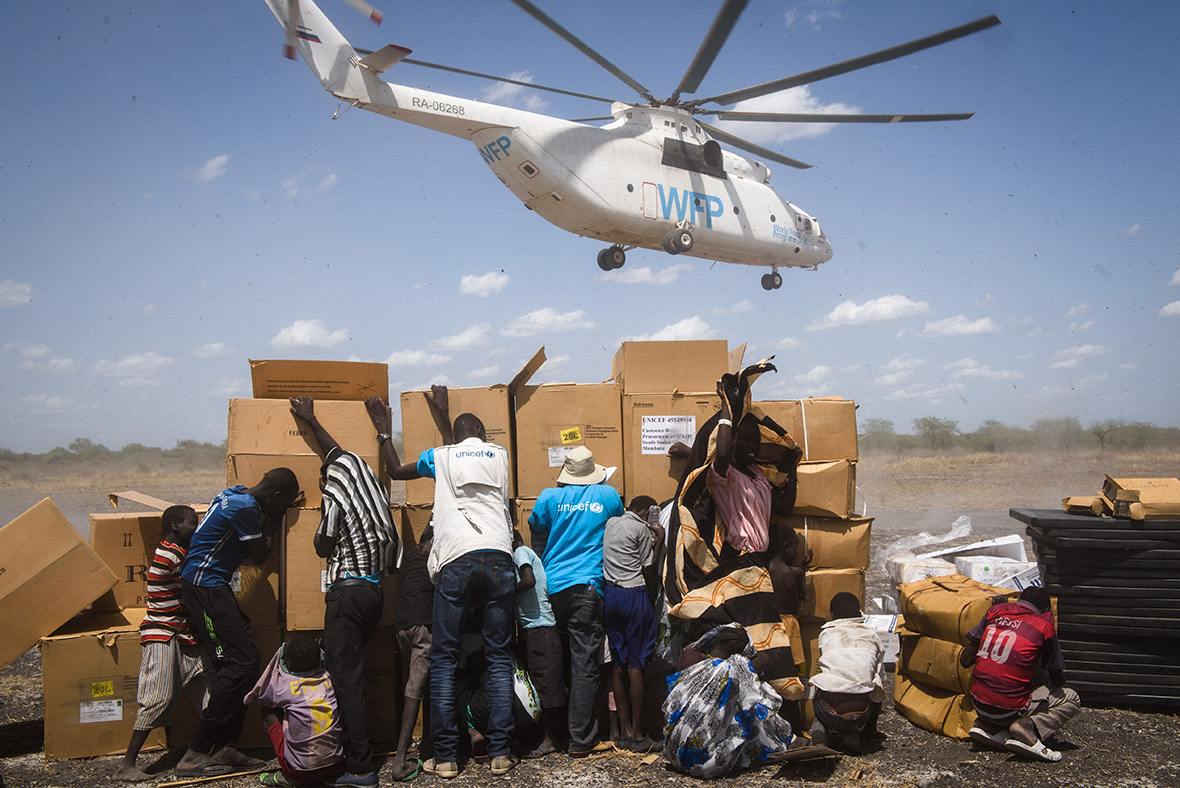
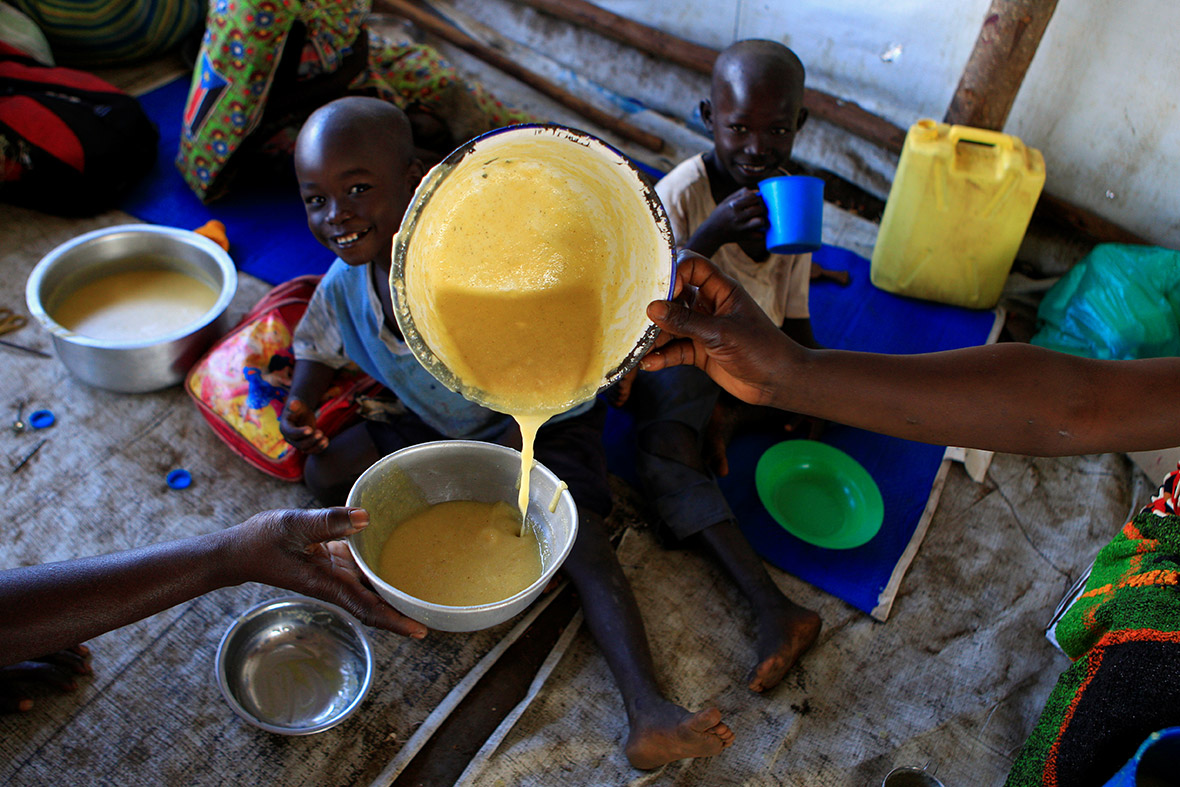
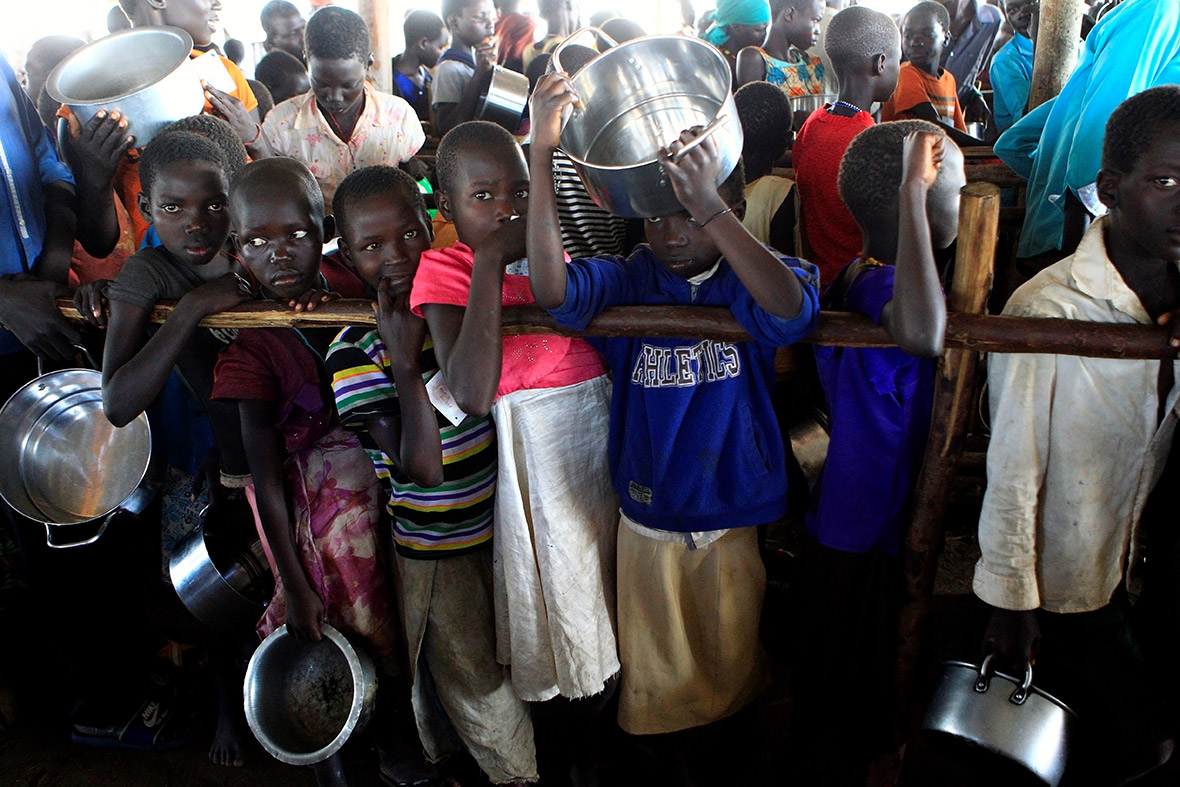



World Refugee Day, observed on 20 June every year, is dedicated to raising awareness of the situation of refugees throughout the world. Every day, thousands of families are forced to flee war and violence, leaving everything behind – except their hopes and dreams for a safer future.
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.






















